What is JAVA?
Java is a programming language that produces software for multiple platforms. It is the most popular programming language for Android smartphone applications, standalone desktop applications and web applications distributed among clients and servers in a network. Java is strictly an object oriented programming language.A Java program is compiled down to bytecode
by the Java compiler. The bytecode can be interpreted by Java virtual machine, which runs on multiple
platforms, Mac, PC or Unix computers into machine code. JIT compiler compiles bytecode into native
machine code “just in time” to run, thus improving the performance of JVM.
1) Google
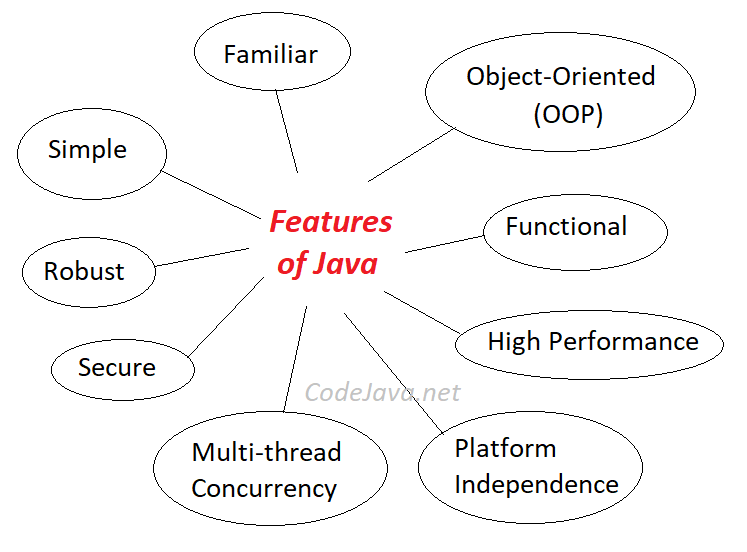
Main features of Java
1) Simple
Java is easy to learn and its syntax is quite simple, clean and easy to understand.The confusing and
ambiguous concepts of C++ are either left out in Java or they have been re-implemented in a cleaner
way.
2) Object Oriented
In java everything is Object which has some data and behaviour. Java can be easily extended as it is
based on Object Model.
3) Robust
Java makes an effort to eliminate error prone codes by emphasizing mainly on compile time error
checking and runtime checking. But the main areas which Java improved were Memory Management
and mishandled Exceptions by introducing automatic Garbage Collector and Exception Handling.
4) Platform Independent
Unlike other programming languages such as C, C++ etc which are compiled into platform specific
machines. Java is guaranteed to be write-once, run-anywhere language.
5) Secure
When it comes to security, Java is always the first choice. With java secure features it enable us to
develop virus free, temper free system. Java program always runs in Java runtime environment with
almost null interaction with system OS, hence it is more secure.
6) Multi Threading
Java multithreading feature makes it possible to write program that can do many tasks simultaneously.
Benefit of multithreading is that it utilizes same memory and other resources to execute multiple
threads at the same time, like While typing, grammatical errors are checked along.
7) Architectural Neutral
Compiler generates bytecodes, which have nothing to do with a particular computer architecture, hence
a Java program is easy to intrepret on any machine.
8) Portable
Java Byte code can be carried to any platform. No implementation dependent features. Everything
related to storage is predefined, example: size of primitive data types
9) High Performance
Java is an interpreted language, so it will never be as fast as a compiled language like C or C++. But, Java
enables high performance with the use of just-in-time compiler.
Uses of Java
1.Android app
Java is the standard language of Android app development, which means the fastest performance and
most native experience.
2.Desktop Apps
Java is probably the easiest way to create cross-platform software these days. The Swing UI toolkit used
to be an alternative to Java developers, but if you’re starting now, skip it and learn JavaFX or SWF
instead.
3.Enterprise systems
High-volume data processing industries (such as banking, financial trading, etc.) use Java for non-legacy
systems, because it is fast, portable, easy to maintain, and are less prone to types of catastrophic bugs in
low-level languages.
4.Embedded Systems
Some areas of embedded space now depend on Java. Examples of embedded systems include digital
watch, factory controller, traffic lights, microcontrollers, hybrid vehicles, and more recently, Internet of
Things devices.
5.Scientific research
Java is mostly used for complex tasks like natural language processing and artificial intelligence. Data
processing, computing, modeling, and simulations are often carried out in languages such as MATLAB
and Python.
Future of Java
From laptops and mobile phones to gaming consoles and scientific computers, Java is everywhere today.
Recent reports from Oracle reveal that there are over 9 million Java developers all over the world. Thus,
Java developers can be assured of a lucrative professional career ahead owing to Java’s strong presence
in the enterprise.







0 Comments